Airspeed Indicator
The airspeed indicator (ASI) is a sensitive, differential pressure gauge that measures and indicates the difference between total and static pressure. These two pressures are equal when the aircraft is parked on the ground in calm air. When the aircraft moves through the air, the pressure in the pitot line becomes greater than the pressure in the static lines. This difference in pressure is registered by the airspeed pointer on the face of the instrument, which is typically calibrated in knots.
The ASI is the one instrument that utilizes both the pitot, as well as the static system. The ASI introduces the static pressure into the instrument case while the total pressure is introduced into the diaphragm. The diaphragm expands or contracts depending on value of the total pressure and static pressure. The diaphragm is linked via a series of mechanical linkages to a pointer on the instrument face.

ASI Markings
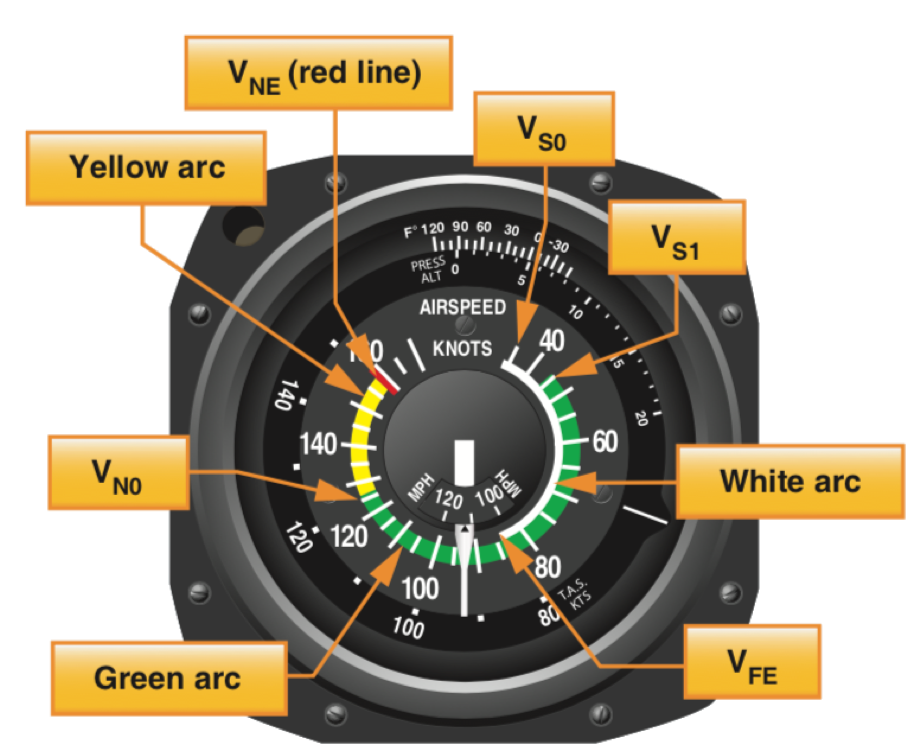
- White Arc: Commonly referred to as the flap operating range since its lower limit represents the full flap stall speed and its upper limit provides the maximum flap speed.
- Lower Limit of White Arc (VS0): The stalling speed in the landing configuration.
- Upper Limit of White Arc (VFE): The maximum speed with the flaps extended.
- Green Arc: The normal operating range of the aircraft.
- Lower Limit of Green Arc (VS1): The stalling speed or the minimum steady flight speed obtained in a specified configuration. For most aircraft, this is the power-off stall speed at the maximum takeoff weight in the clean configuration
- Upper Limit of Green Arc (VNo): The maximum structural cruising speed. Do not exceed this speed except in smooth air.
- Yellow Arc: Caution range. Fly within this range only in smooth air and then only with caution.
- Red Line (VNE): Never exceed speed. Operating above this speed is prohibited since it may result in damage or structural failure.
Types of Airspeeds
- Indicated Airspeed (IAS): The direct instrument reading obtained from the ASI, uncorrected for variations in atmospheric density, installation error, or instrument error.
- Calibrated Airspeed (CAS): IAS corrected for installation error and instrument error. Although manufacturers attempt to keep airspeed errors to a minimum, it is not possible to eliminate all errors.
- True Airspeed (TAS): CAS corrected for altitude and nonstandard temperature.
- Ground Speed (GS): The actual speed of the airplane over the ground. It is TAS adjusted for wind.
