IFR Altitude Limitations [DELETE]
Within controlled airspace, ATC is not permitted to approve or assign any IFR altitude below the minimum IFR altitude. To ATC, the minimum IFR altitude is the lowest IFR altitude established for use in a specific airspace.
- Minimum IFR Altitude: The lowest IFR altitude established for use in a specific airspace. Depending on the airspace concerned, the minimum IFR altitude may be a minimum obstacle clearance altitude (MOCA), a minimum en route altitude (MEA), a minimum sector altitude (MSA), a minimum vectoring altitude (MVA), a safe altitude 100 NM, an area minimum altitude (AMA), a transition altitude or a missed approach altitude. The minimum IFR altitude provides obstacle clearance but may or may not be within controlled airspace.
- Minimum En Route Altitude (MEA): The altitude above sea level (ASL) between specified fixes on airways or air routes that assures acceptable navigational signal coverage and that meets the IFR obstacle clearance requirements.
- Minimum Obstacle Clearance Altitude (MOCA): The altitude above sea level (ASL) between specified fixes on airways or air routes that meets the IFR obstacle clearance requirements for the route segment in question.
- Minimum Sector Altitude (MSA): The lowest altitude that will provide a minimum clearance of 1,000 feet under conditions of standard temperature and pressure above all objects located in an area contained within a sector of a circle with a 25 NM radius centred on a radio aid to navigation or a specified point.
- Safe Altitude 100 NM: The lowest altitude that may be used under instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) that will provide a minimum vertical clearance of 1,000 feet or, in a designated mountainous region, 1,500 or 2,000 feet, as appropriate, rounded up to the next 100-ft increment, under conditions of standard temperature and pressure, above all obstacles located in an area contained within a radius of 100 NM of the aerodrome geometric centre.
- Area Minimum Altitude (AMA): The lowest altitude that may be used under instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) that will provide a minimum vertical clearance of 1000 ft or, in a designated mountainous region, 2000 ft, rounded up to the next 100-ft increment, under conditions of standard temperature and pressure, above all obstacles located in the area specified.
- Minimum Vectoring Altitude (MVA): The lowest altitude for vectoring aircraft by ATC that meets obstacle clearance and radio coverage requirements in the airspace specified.
A controller is not permitted to clear an aircraft flying on an airway at an altitude below the MEA. However, flight below the MEA, but not below the MOCA, may be approved when specifically requested by the pilot in the interest of flight safety (e.g.: icing/turbulence), to conduct a flight check, for MEDEVAC, or when navigating using GNSS.
Navigational signal coverage is not guaranteed below the MEA; when navigating using NAVAIDS, the pilot should ensure that the aircraft is within, and will remain within, the lateral limits of the airway before requesting approval to fly below the MEA. It should also be noted that flight below the MEA does not guarantee the aircraft will remain in controlled airspace.
Minimum Altitudes to Ensure Obstacle Clearance
The pilot-in-command of an IFR aircraft shall, except when taking off or landing, or when being radar-vectored by an air traffic control unit, ensure that the aircraft is operated at or above:
- The MOCA, when the aircraft is on an airway or air route
- The minimum altitude established by the Minister to ensure obstacle clearance and specified on an IFR chart, when the aircraft is within airspace in respect of which such a minimum altitude has been established.
When an aircraft is not being operated on an airway or air route or within airspace in respect of which a minimum altitude has been established, the pilot-in-command shall ensure that the aircraft is operated at or above:
- An altitude of 1,000 feet above the highest obstacle located within a horizontal distance of five nautical miles from the estimated position of the aircraft in flight
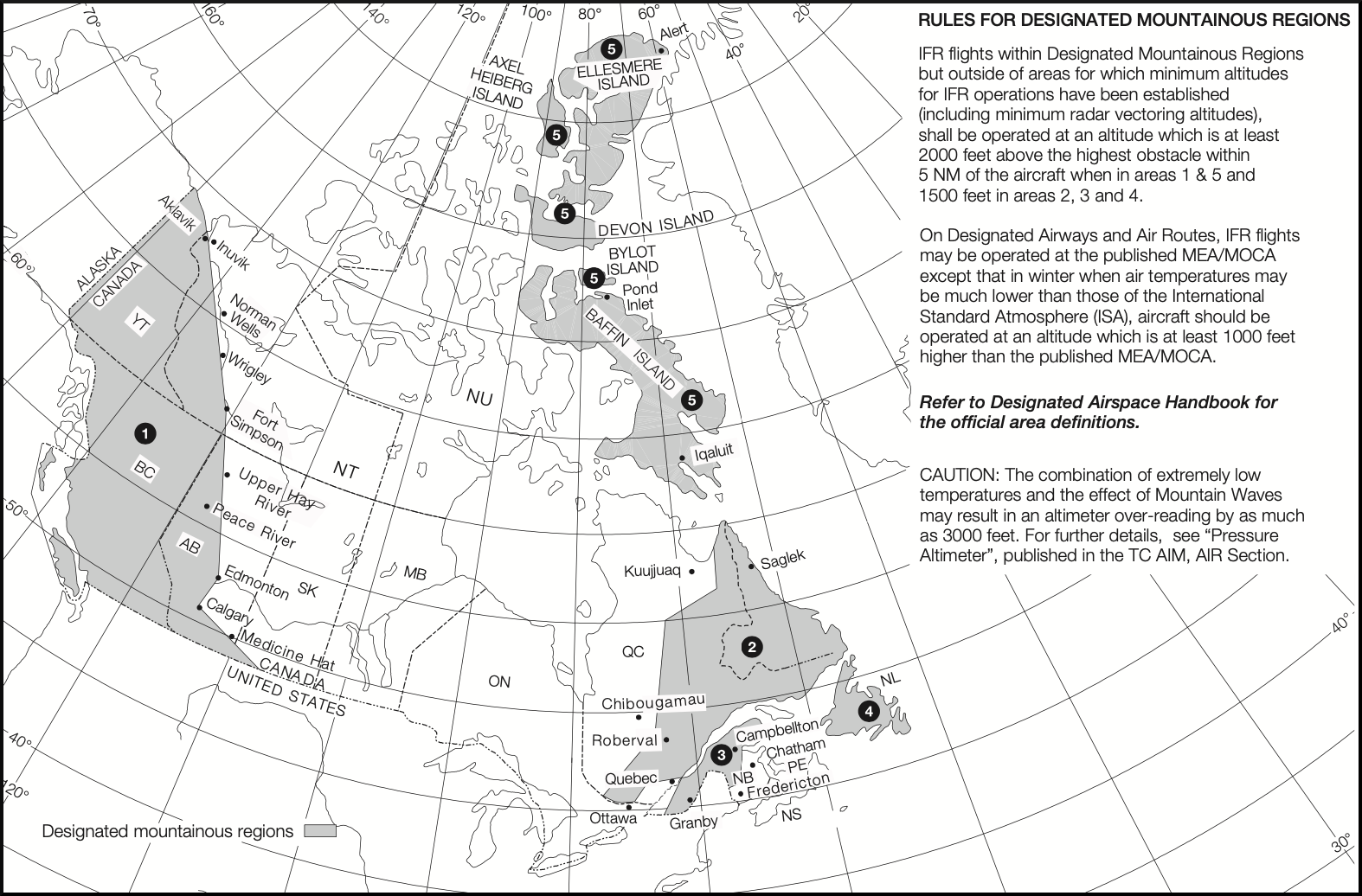
- An altitude of 2,000 feet above the highest obstacle within a horizontal distance of five nautical miles from the estimated position of the aircraft in flight if in a region designated as a mountainous region 1 or 5
- An altitude of 1,500 feet above the highest obstacle within a horizontal distance of five nautical miles from the estimated position of the aircraft in flight if in a region designated as a mountainous region 2, 3 or 4
REFERENCES AIM RAC 8.6.1 Minimum IFR Altitudes 602.124 Minimum Altitudes to Ensure Obstacle Clearance
